What is Coaching?
Coaching is different to mentoring or counselling, though it does share some techniques with both, and is solutions-focused and results-orientated.
Leaders who coach their staff appropriately, individually or in teams, report effective results. It can be more time consuming in the short term than other methods of training, improving or developing your team members, but coaching pays dividends overall. It is acknowledged as one of the best ways to get improved performance from your team.
You are also responsible for behaving ethically in the way you relate to your team member:
‘The effective coach or mentor is responsible for considering their ethical perspective, and agreeing with the client how they will work together. It is the responsibility of the coach or mentor to create a climate where ways of working can be discussed. It is their responsibility to monitor their standards of practice and reflect on how they are working with clients. It is also their responsibility to be aware of other sources of help that they or their client might call upon if needed.’
Connor, M. and Pokora, J. (2012)
The Coaching Contract
It is a ‘living’ document that can be reviewed and amended at any time, and is likely to include the following:
- Expectations of each other and of the relationship
- Coaching aims and objectives
- Any confidentiality issues that may arise
- Duration of the coaching relationship
- Location
- Roles and responsibilities of both parties
- Responsibilities either party may have outside the coaching relationship, e.g. to other managers
- How the coaching relationship will end
- The notice acceptable to both parties should the relationship be cancelled.
The Coaching Context
The coaching relationship is fundamental to the success, or otherwise, of coaching. It is essential that a trusting relationship is established, and that expectations of, and parameters to, the coaching process are established from the beginning.
You should also take time to research your team member as a background knowledge of your team member gives them confidence and builds trust and enables coaching to be better focused.
An initial meeting is important to establish ground rules and an understanding of how you will work together.
You should also make yourself aware of any issues in the wider team member context that may impact on your coaching relationship, such as:
- The level of support from line managers or other stakeholders
- The organisational culture
- Who you must contract with
- The systems, structures and processes in place to support the coaching relationship
- What your team member wants, or needs, to learn (Learning Goal)
- The knowledge, skill or attitude to be developed to attain the Learning Goal
- Resources or support required
- Success criteria
- Target dates for review and completion
Coaching Skills and Techniques
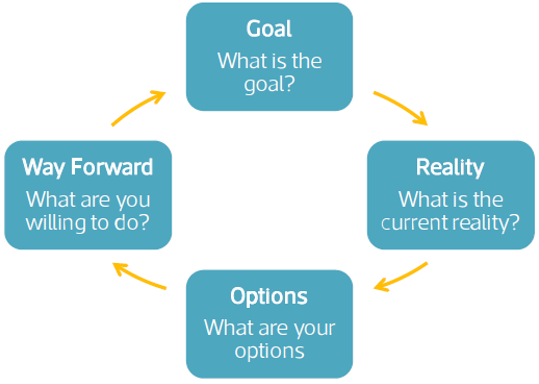
A well-established sequence of questions is offered by the GROW model:
Potential Barriers to Coaching in the Workplace
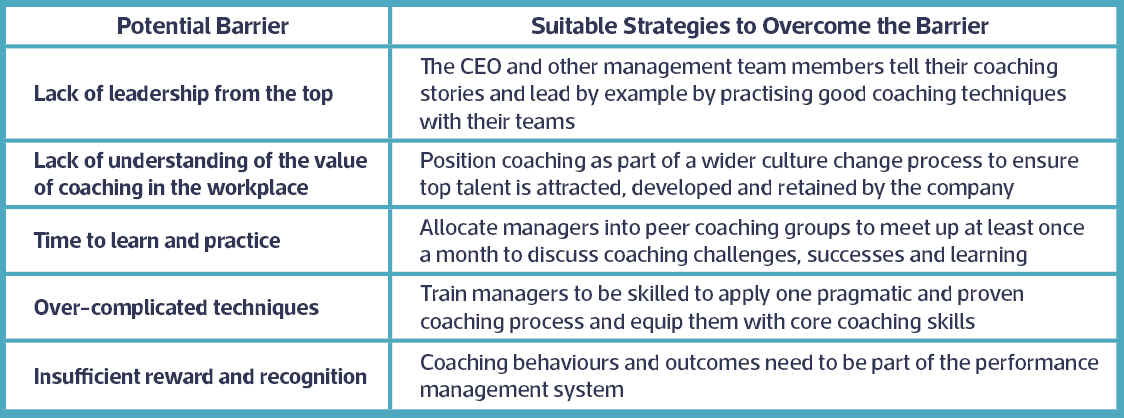
Adapted from Brook, J. (2015)
References
Brook, J. (2015). Common Barriers to Coaching Culture www.strengthscope.com/common-barriers-coaching-culture-overcome/ (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Connor, M. and Pokora, J. (2012). Coaching and Mentoring at Work: Developing Effective Practice McGraw-Hill Education
Fairley, M. (2021). Why coaching matters in leadership development Why coaching matters in leadership development - Roffey Park Institute (Accessed 9/10/2022)
Freifeld, L (2012). 6 Steps to Sustain a Coaching Relationship 6 Steps to Sustain a Coaching Relationship (trainingmag.com) (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Hill, M (2016). Beginning a Coaching Relationship Beginning a Coaching Relationship | British School of Coaching (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Lowisz, S. (2019). The Keys To Effective Coaching The Keys To Effective Coaching (forbes.com) (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Newby, A (2017). Does insight into coachee context matter? Part 1 – benefits Does insight into coachee context matter? Part 1 – benefits | Newbycoach thoughts (wordpress.com) (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Newby, A (2017). Does insight into coachee context matter? Part 2 – drawbacks Coachee context | Newbycoach thoughts (wordpress.com) (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Starr, J (2011). The Coaching Manual Pearson Education
Sime, C. (2019). How Does Coaching Actually Help Leaders? How Does Coaching Actually Help Leaders? (forbes.com) (Accessed 9 October 2022)
Want to get recognised for your coaching skills?
Get accredited with coaching conversations, a practical assessment to evidence that you understand and practice coaching approaches at work. The only product of its kind where you are measured on your actual coaching discussion. No written assessments.
Are you a good coach? Test yourself with our Scorecard.
If you’re a member, you can test yourself on your Coaching skills and see if you meet the standard.
Spotlights
Further Resources
From the blog







